BOCA CHICA, Texas — After an initial hold at T-42 seconds, SpaceX successfully launched the Super Heavy rocket and the Starship spacecraft on its second attempt.
The rocket lifted off from its Starbase in Boca Chica, Texas, three days after the first attempt was scrubbed due to a valve issue.
The first attempt
On Monday, April 17, SpaceX stopped the first launch attempt nine minutes before the 9:20 a.m. EDT (8:20 a.m. CT) launch window was set to open.
SpaceX CEO and founder Elon Musk tweeted out that a pressurant valve seemed to have frozen during the cryogenic propellant loading of the nearly 400-foot-tall Super Heavy rocket and stacked Starship.
During a live teleconference, Kate Tice said the issue happened in the first stage of the rocket.
Tice, the quality systems engineering manager at SpaceX, called Monday’s attempt a “wet-dress rehearsal.”
About the Super Heavy and Starship
The Starship is designed to carry a crew of 100 people and cargo to Earth orbit, the moon and eventually Mars, according to the ship’s user guide.
Both the Super Heavy rocket, with its 33 Raptor engines fueled by sub-cooled liquid oxygen and liquid methane, and the Starship are designed to be reusable.
And speaking of engines, the Starship itself has some under the hood, figuratively speaking.
“Starship will be powered by six engines, three Raptor engines, and three Raptor Vacuum (RVac) engines, which are designed for use in the vacuum of space,” SpaceX described.
Ready for take off
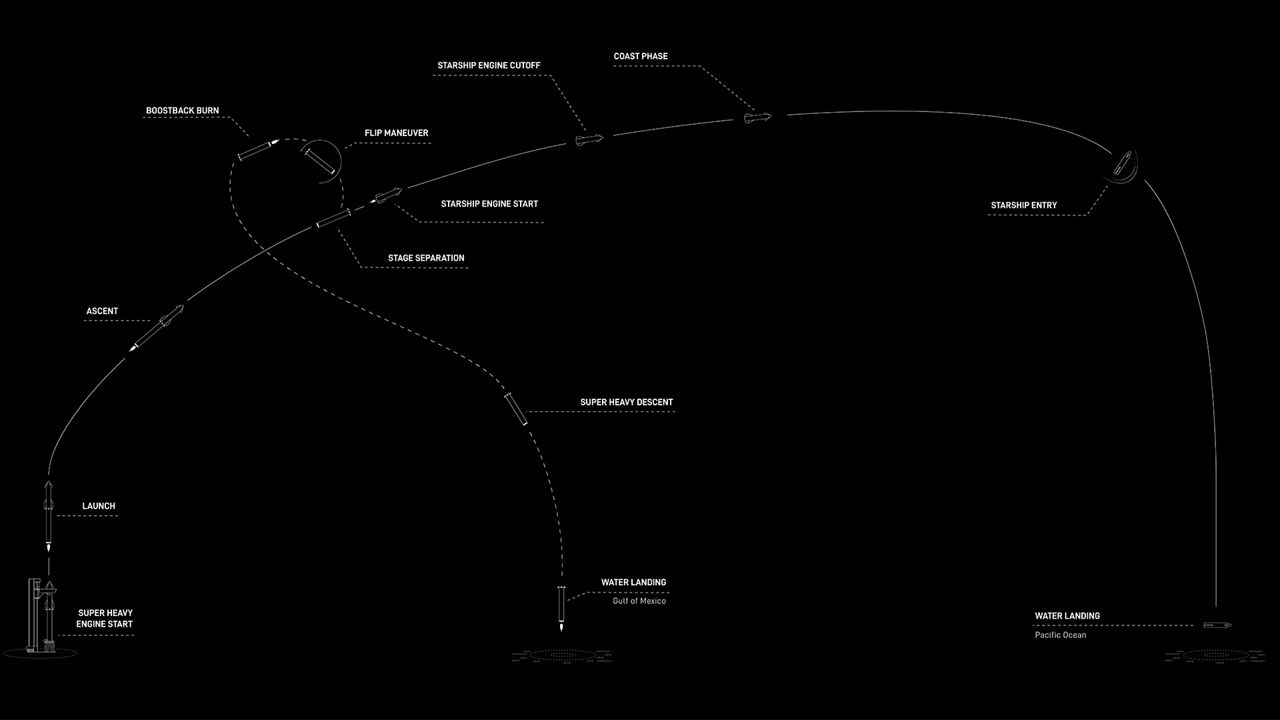
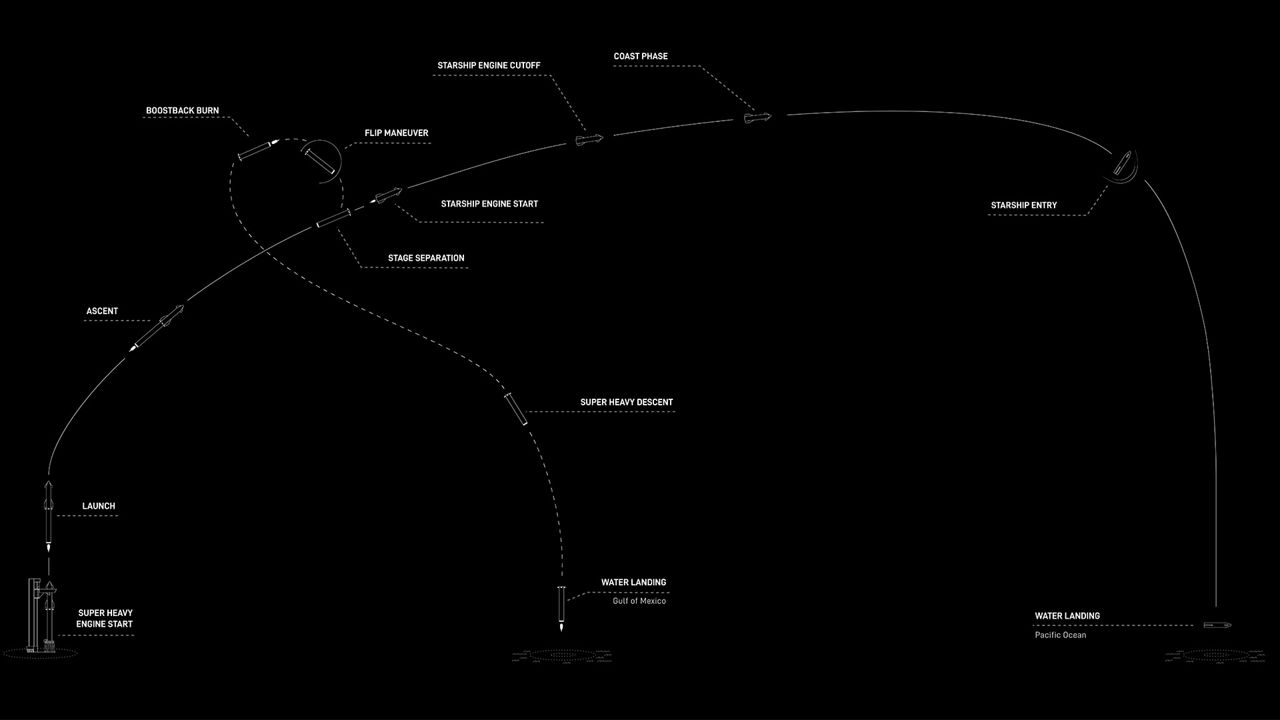
For the flight debut on Thursday, the Super Heavy rocket, called Booster 7, will be pumped with 3,400 tons of propellant while Starship 24 will receive 1,200 tons of fuel.
Once liftoff happens, there will be a series of measured successes.
In a fully successful flight, the rocket will reach the point of greatest stress, known as ‘Max Q,’ about 55 seconds into flight. The Super Heavy booster will separate at about 2:52 minutes into the mission. The booster will conduct a boostback burn, followed by a landing burn and splash down in the Gulf of Mexico about eight minutes after liftoff.
Starship itself won’t reach orbit (about 146 miles in altitude expected), but will instead splash down off the coast of Hawaii about an hour and a half after leaving Texas.
That information and the details of the launch can be found here.
Watch the test flight here